Tumor Surgery
شنبه 1 اردیبهشت 1397
بازدید: 1425
Eyelid and orbital tumors
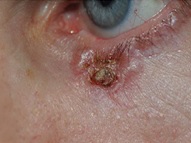
Tumors are abnormal tissue masses. It is usual for patients when they hear the word “tumor” to associate it with something bad. But it is not always like that. Sometimes, tumors are proliferations or growths of benign cells, so they are not cancerous; in other cases, tumors are proliferations of malignant cells, thus being cancerous.
- •Orbital tumors are those located in the orbital cavity, which is the cavity surrounding the eye. This cavity has muscles, blood vessels… And any of these structures may suffer from a tumor.
What kind of tumors are there? Can they be malignant?
There are lots of tumor types, both palpebral and orbital. There are benign and malignant tumors, and even some that may start being benign and they later become malignant. Therefore, when faced to a tumor suspicion, a monitoring must be made in order to know whether the tumor may or not become malignant.
Causes
As they are many kinds of tumors, the production mechanism for each one of them is different. But in eyelid tumors, the risk factor is sun damage. Skin highly damaged by the sun causes higher chances of suffering a skin cancer. It is very important to use a proper sun protection. We should:
- •wear sunglasses
- •use sunscreen (there are face sunscreens that may be applied on eyelid skin)
- •and avoid sun exposure during the intense sun hours from 12h to 15h.
Patients who already suffer skin cancer in other body areas, especially in the face skin should go immediately to the specialist when they discover any lesion in their eyelids that is not painful but bleeds or itches, in order to obtain an early diagnosis.
Diagnosis
When a patient arrives at the consultation and we see a lesion that is suspected of being malignant and we believe it may be cancerous, we’ll need to know the type of tumor we are faced to, and confirm if it is indeed cancerous.
The most reliable way we have to know what kind of lesion we are facing is by means of a biopsy. Biopsies allow us to collect a piece of tissue, analyze it and classify it. This is really important, as depending on the type of tumor, the treatment could differ.
If eyelid tumors are small and we can remove them completely with an only surgical intervention, we’ll do it and wait the biopsy results. Both if it is cancerous or not, we’ll be reassured because we have completely removed it.
In case of large tumors, biopsies serve to confirm whether it is cancerous and, if so, proceed to the complete removal of the lesion, which may require sometimes complex reconstruction by means of grafts or flaps.
In case of orbital tumors, it isn’t always possible to perform a biopsy. Many of them are diagnosed by clinical features the patient has and the results of image tests, such as CT or MRI procedures…
Treatment
The treatment will depend on the tumor type. Small benign eyelid tumors may be easily removed with a small surgery. But other larger tumors may require more complex surgeries. Malignant tumors must be completely removed; sometimes this is quite easy, but other times it requires complex surgeries performed in two or three times.
In terms of orbital tumors, the treatment will be different, and will depend on the tumor type. Its sensitive location means they cannot always be removed. Those providing easy access to the surgeon may be removed, but with those located at difficult access areas, monitoring will be necessary, and they will need to be assessed at each time in order to determine how to proceed. They do not always require a surgical treatment. The most frequent orbital primary tumor is lymphoma. It is diagnosed through a biopsy, but its treatment isn’t surgical, but radiotherapy or chemotherapy is instead used, depending on histological type.
In case of malignant eyelid tumors, if we achieve to remove the whole tumor and the healthy tissue that surrounds it, the success rate will be high, and chances it reappears are low. However, we monitor them in consultation after the tumor removal for an early detection of any possible recurrence or reappearance, in which case a new intervention could be performed.
In case of orbital tumors, the success rate will vary depending on the tumor type.
دیدگاه های ارسال شده توسط شما، پس از تایید مدیر سایت در وب سایت منتشر خواهد شد.
پیام هایی که حاوی تهمت یا افترا باشد منتشر نخواهد شد.
پیام هایی که به غیر از زبان فارسی یا غیر مرتبط با خبر باشد منتشر نخواهد شد.